HEPA Filter Definition



A throwaway extended-media dry-type filter in a rigid frame having minimum particle collection efficiency of 99.97% for 0.3 micrometer particle size.

HEPA Filter Construction



- Filter material is boron silicate fiber
- Separators - thin and rigid to separate layers of filter material – often made of aluminum
- Frame - rigid and heavy to support filter material and separators - often made of wood

HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) Filters



 Particle Collection Mechanisms Particle Collection Mechanisms
- Occur at the microscopic level
- Deep inside the filter medium
- Particles stick to the filter medium
- Particles stick to previously trapped particles
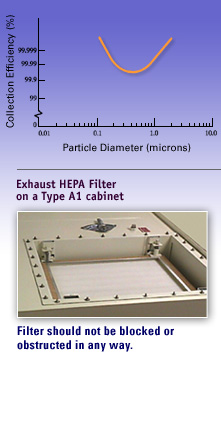
Particle size influences the collection (capture) mechanism
- Larger particles
- Smaller particles (less than 0.3 micrometer)
MORE than 99.97% effective on particles GREATER than and LESS than 0.3 micrometer in size. The 0.3 micrometer is the ‘most penetrating particle size’
HEPA filters DO NOT filter out gasses and vapors, they only filter out particulates



 |